After several years of sluggish growth, telecom businesses continue to be shaken up as digitization re-shapes the market landscape. They need to hasten their race to develop value while continuing to reduce costs in connectivity and also differentiate with access that is ultrafast to flourish in the years to come.
The telecommunications industry isn’t made up of peddling television offerings, office phones, and mobile. Emerging and promising technologies, for example, 5g and SD-wan, are expanding the sector and making your competition fiercer.
- 80% of the world’s population will be to the net in five years
- 5 billion people are connected to mobile
- 1/3 of customers will use virtual reality from 2020
- 20 billion smart objects will be connected to the internet by 2020
After looking at the current global telecom statistics, the most significant carriers of the industry should find a need to return for their core telecom roots to boost profitability and enable their customers to connect longer endpoints.
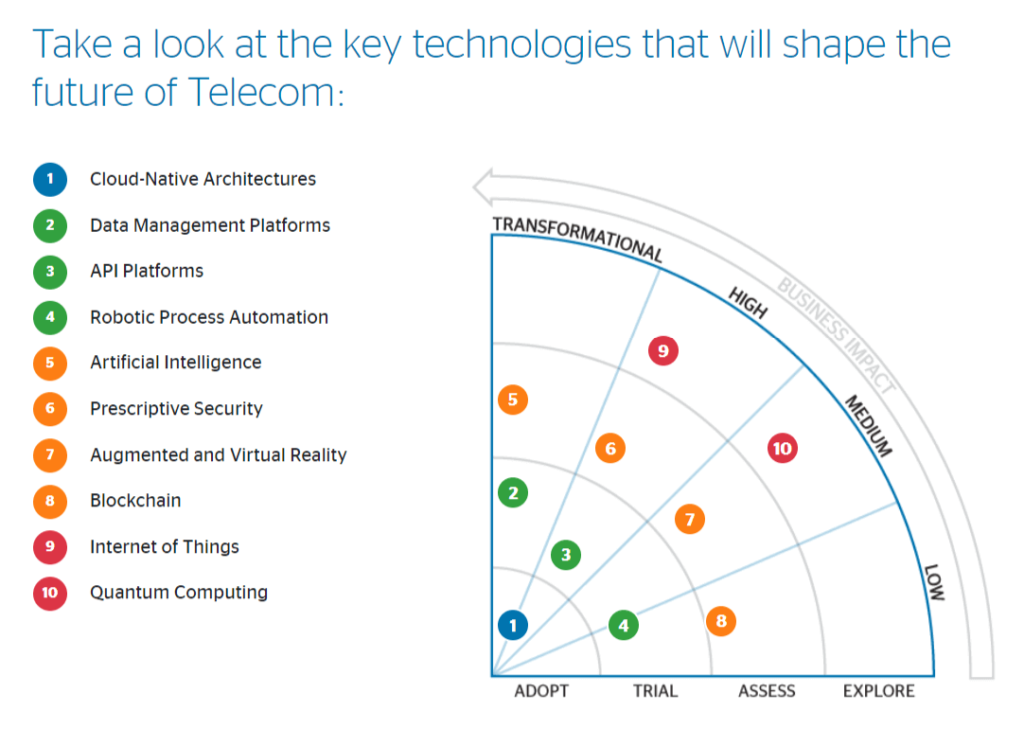
Here are the seven biggest telecommunications industry trends that’ll likely be making their effect in the marketplace in 2020.
1. 5G Telecom
The fifth-generation of wireless tech, 5g, is gradually working its way onto the telecom scene and promises faster download speeds, high network visibility, and a significant impact on lifestyle for both consumers and businesses, especially as technologies like 5g make new use-cases potential, such as smart cities and self-driving cars.
2. AI, ML, and Automation
The telecoms business is akin to the tech industry, producing platforms that are of reliability. Still, they need to be continued to push the boundaries and limitations of technology. This allows existing clientele and prospects to recognize that there is a business prepared for future years.
Talking about the investments in the field of Artificial Intelligence, machine learning, marketing automation, and, if integrated into the platform and services, provides a company an edge from the competition.
Telecommunications is one of the industries where artificial intelligence is being used by many businesses. Through chatbots and assistants, and also the information that is gathered by these tools is used to offer satisfaction to the customer, build a good brand reputation and improves retention rate.
Artificial Intelligence is essential for the predictive and optimization maintenance of telecommunications companies’ networks. Besides, through predictive analytics, artificial intelligence can make it possible for telecoms to authenticate actionable business insights out of the quantities of data daily, they gather.
3. IoT (Internet of Things)
Arguably one of the most significant trends to impact the telecom market could be the web of things, which joins endpoints, devices, and assets that have been able to communicate with a network.
IoT is rapidly learning to be a massive supply of revenue for the carriers, too, and those amounts are merely likely to rise since a service provider’s job growth in IoT earnings heading right into 2020.
Internet of things technologies help telecoms monitor data and base channels. This helps ensure minimal downtime for your network. The industry is uniquely poised to build up and offer their services since telecom is so instrumental in providing IoT infrastructure.
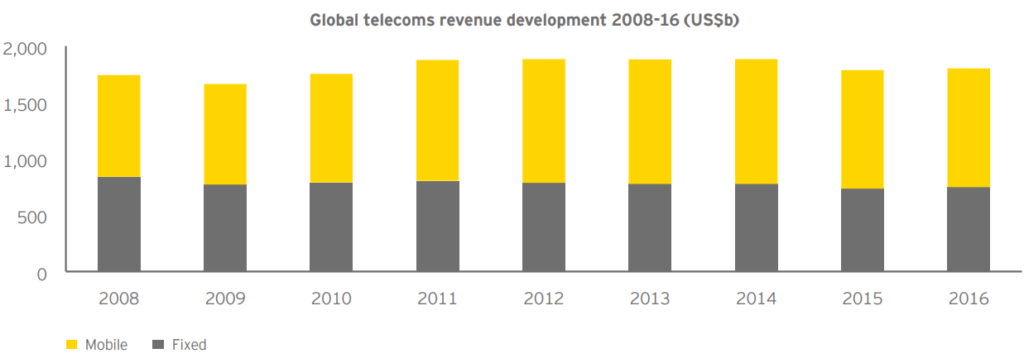
From 2020, joined devices across all technologies will soon reach 20.6 billion, based on a study from market research firm Gartner.
Since IoT technology contributes to many more devices on the network, you will find opportunities for security and privacy breaches that occur, so telecoms will need to plan and prepare security implementations for this.
Therefore what does this imply for telecom or ISP? It is estimated that the ratio between both human and device communications will probably soon be 30:1. This usually means that operators can expand their subscriber base to more than a trillion machines and objects or into 50 billion.
Also read: – Inventions that changed the broadcasting forever
– App that steals money from Android users mobile.
4. Big-Data
It is indisputable that telecommunications organizations are collecting and generating volumes of data from mobile devices and apps, wearables, and much more – wireless data is forecast to continue to rise through the 2020s -nonetheless, it’ll be the organizations which utilize it to their advantage that will survive.
Telecommunications businesses need to ensure that their networks can proceed with massive amounts of data through their system efficiently and continue to support the new technology. When assessed and relied upon, big data can help telecoms build a stronger business.
Telecoms also will need to address the unique security challenges that have arisen. The analyzed data will determine the increase customer assistance and evaluate new services and products, as well as monitor and optimize your network.
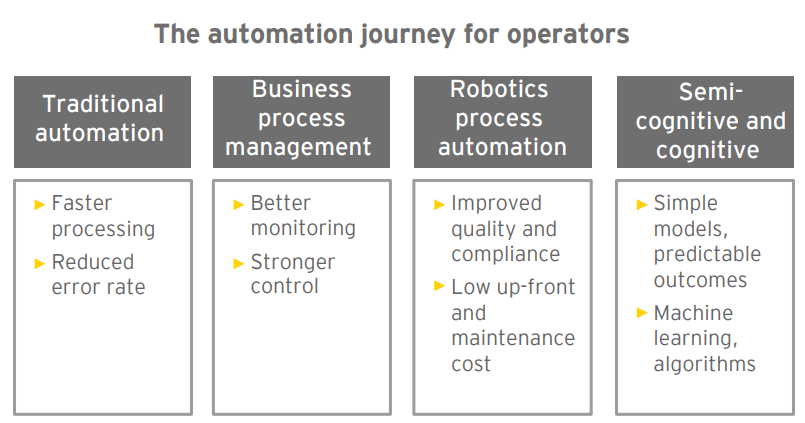
5. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
When telecoms deploy, RPA. Tasks such as errors and costs are significantly reduced while customer service and operational efficiency are fostered.
The telecommunications business has as it seems to serve it 17, one among the maximum adoption rates for RPA technology.
RPA provides high levels of scalability and ability for telecoms and can take over many tasks like report generation, responding to customer questions, order processing, price tracking, and more.
6. Cloud Computing
Not only do telecoms are now become a cloud service provider; however, they can make use of the cloud services themselves. When cloud technology is adopted by telecoms and switch business functions that are essential to the cloud, they enjoy the cloud’s efficiency.
Cloud computing’s pay-per-use service model helps telecoms adapt to market demands, reduce their costs, and present new services. The cloud offers savings of cost-effectiveness, scalability, and scale into telecoms.
7. Cyber-Security
As a result of telecoms of sensitive data on advanced networks that act as gateways to new companies and because they build and operate infrastructure, telecoms are increasingly a target for cyber criminals.
We ignore the services that are enabled by telecoms email, including hosted phone systems and video calls and messaging before we comprehend just how reliant we are about those services and experience an outage.
Cyber-attacks such as a distributed denial-of-service to attacks such as malware, prepare for the security hurdles that’ll represent, and the near long run of 5g and also telecoms need to protect themselves. This includes not only the best infrastructure in place; however, the talent and processes to encourage resiliency when attacked.
Currently, there is room for advancement in the industry’s response to a cyber-attack. Even false claims of assault can damage a telecom’s standing, besides, a business impact in terms of time and investment.
Conclusion:
According to these trends, communication companies have been aroused to transform themselves into a platform of opportunities harnessing the seven digital forces – 5G Telecom, Artificial Intelligence, IoT, Big-Data, RPA, Cloud Computing, and Cyber-Security solutions.

The third and third fourth-largest wireless carriers from the use, sprint, and T-Mobile are likely to come along early next season after the FCC granted both businesses consent in November.
Market saturation would also be a factor for some age groups. For example, an older person will soon probably be forced into employing these technologies and can likely consume their carriers imagined or vastly more bandwidth than that they. The remaining percentages of market penetration will be achieved. Since this occurs, and also, the marketplace is likely to be saturated.




